An important tool for detecting and treating diseases caused by viruses and bacteria is their rapid and reliable identification. The crux of many tests: rapid antigen tests provide results quickly, but with great inaccuracy; PCR tests, however, are more accurate, but take considerably longer.
Our development
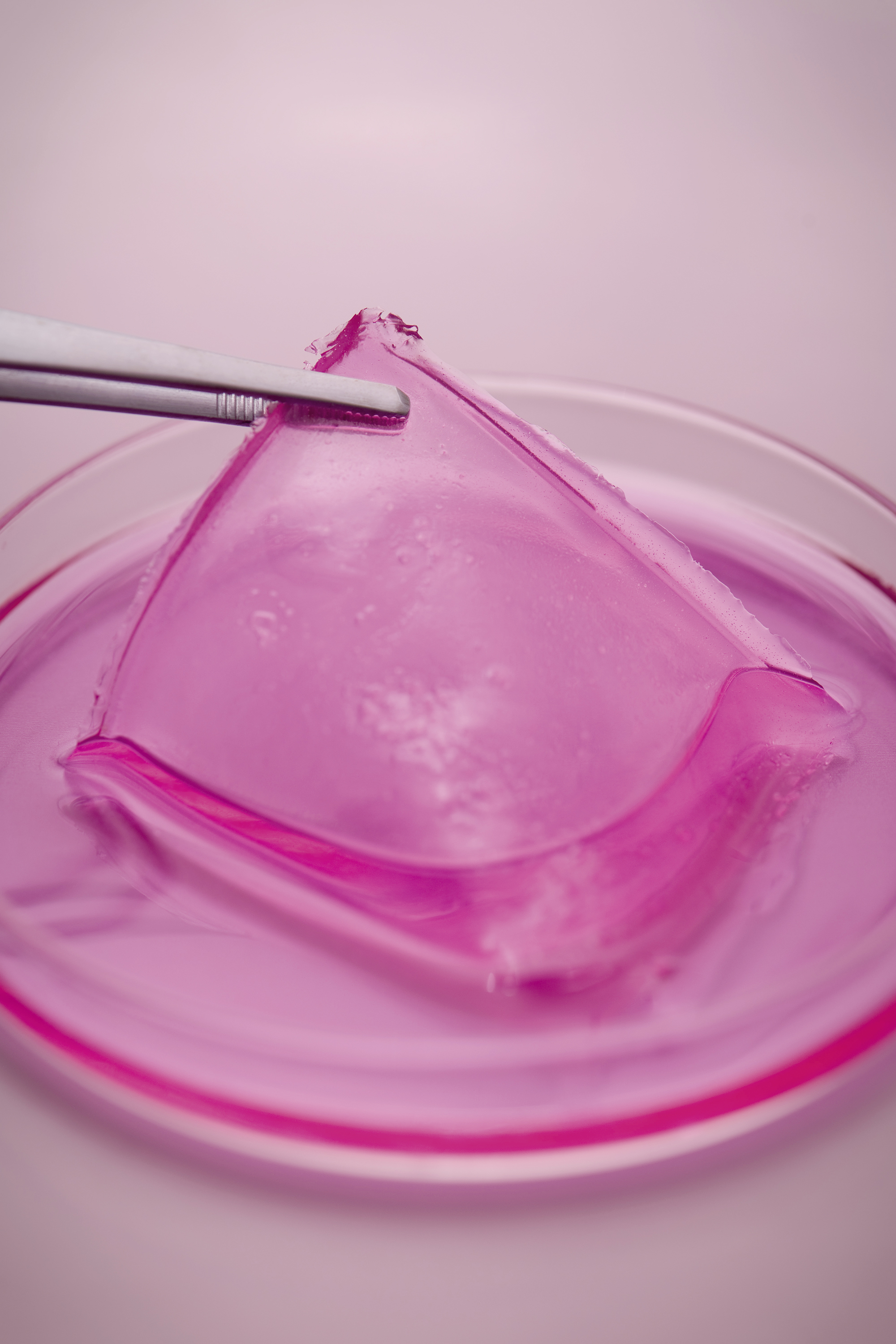
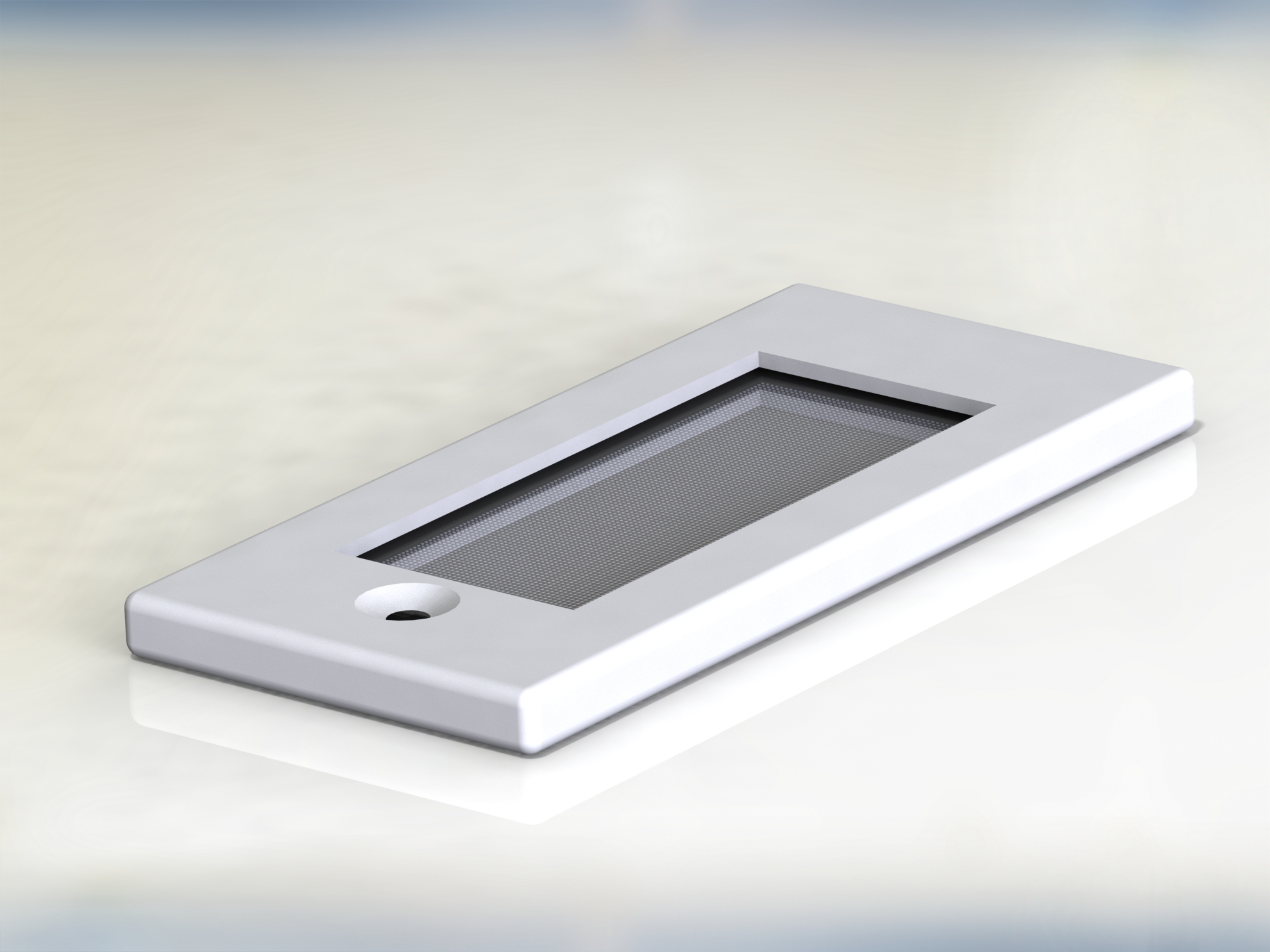
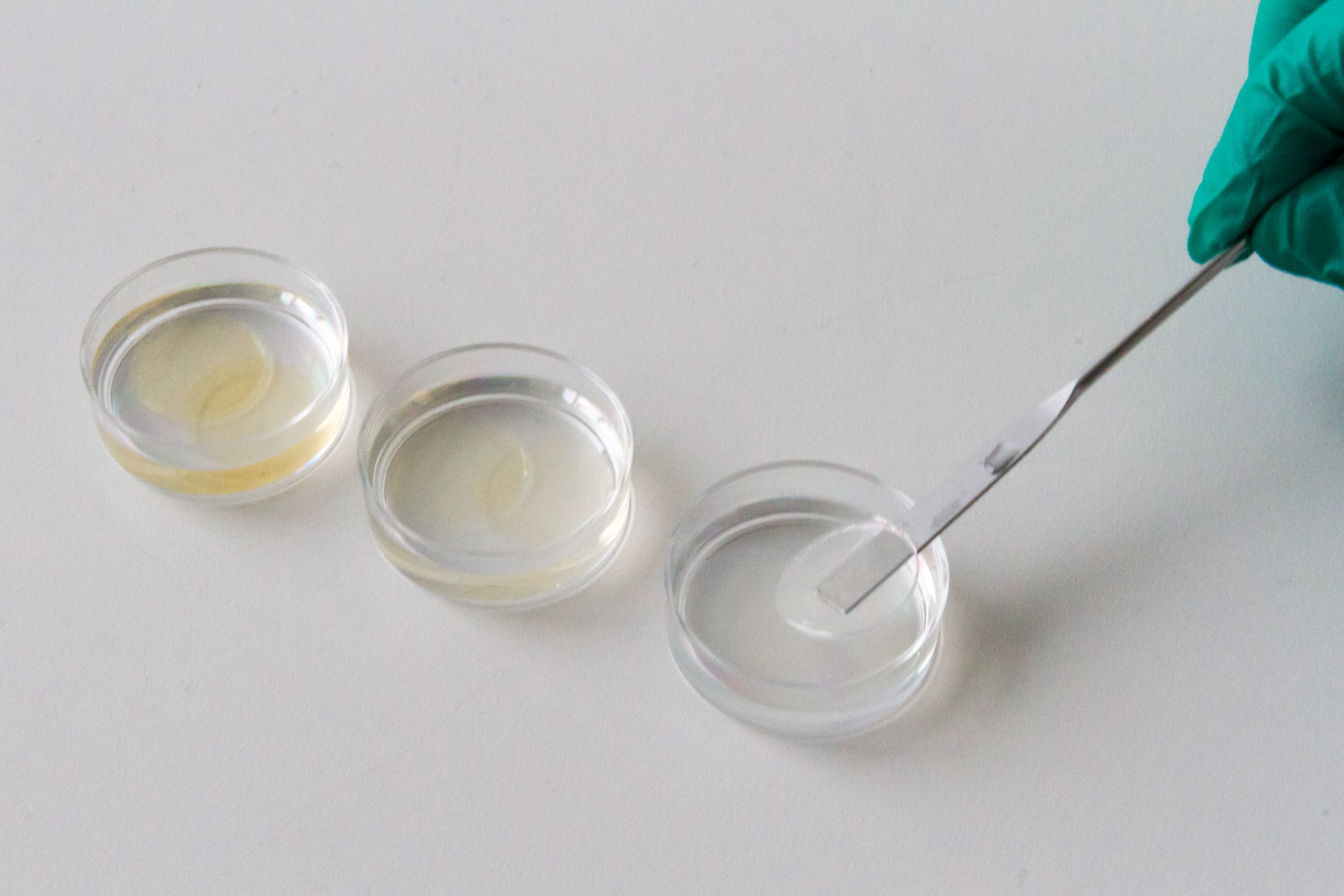
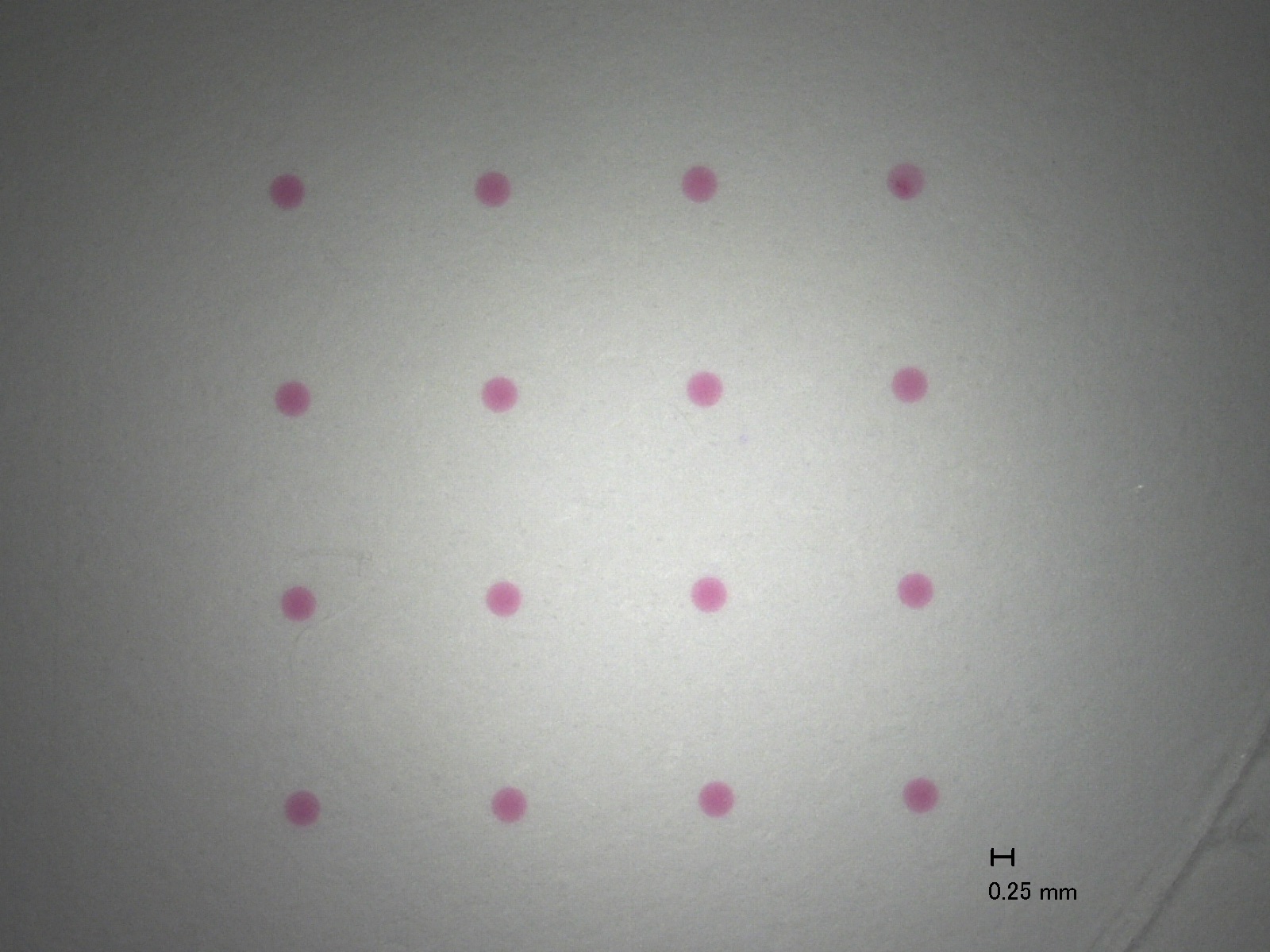
Fraunhofer IGB, in cooperation with the Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology IPT and the Fraunhofer Center for Manufacturing Innovation CMI in Boston (USA), has developed an alternative that is both fast and accurate. In our approach, we use the RT-LAMP technology (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification) for the rapid amplification of the viral or bacterial RNA for subsequent detection. The highlight: by combining it with our patented, printable hydrogel, the test becomes much more sensitive and many pathogens can be detected simultaneously (multiplexing).
Advantages and technological readiness
Our solution distinguishes itself from other current products because of various advantages:
- Fast and accurate result
- No sample preparation required, which means that tests could also be carried out at home
- Printing process enables spatial multiplexing allowing testing for many different pathogens within one examination
The feasibility of our approach has been successfully demonstrated (TRL 3-4). The next step is to optimize the sensor layout and transfer it to cost-effective, scalable production processes.
Collaboration
Since we developed the system as a modular system, it is easily adapted to customer-specific issues such as new pathogens. If you are interested in the joint development of a market-ready product, please do not hesitate to contact us.
We see areas of application wherever information is needed quickly about whether and with which pathogens a person is infected. This can be the case, for example, at entrance control in areas with an increased risk of infection (hospitals, care facilities). By adjusting the pathogen spectrum on the sensor, our system is also suitable for monitoring microorganisms in the environment and food production or for quality control in pharmaceutical production.
One of the main functions of our patented hydrogel is the stabilization of biomolecules (proteins, enzymes). The hydrogel therefore also offers great advantages for the development of other products, e.g. other test assays, formulations or surface modifications.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB