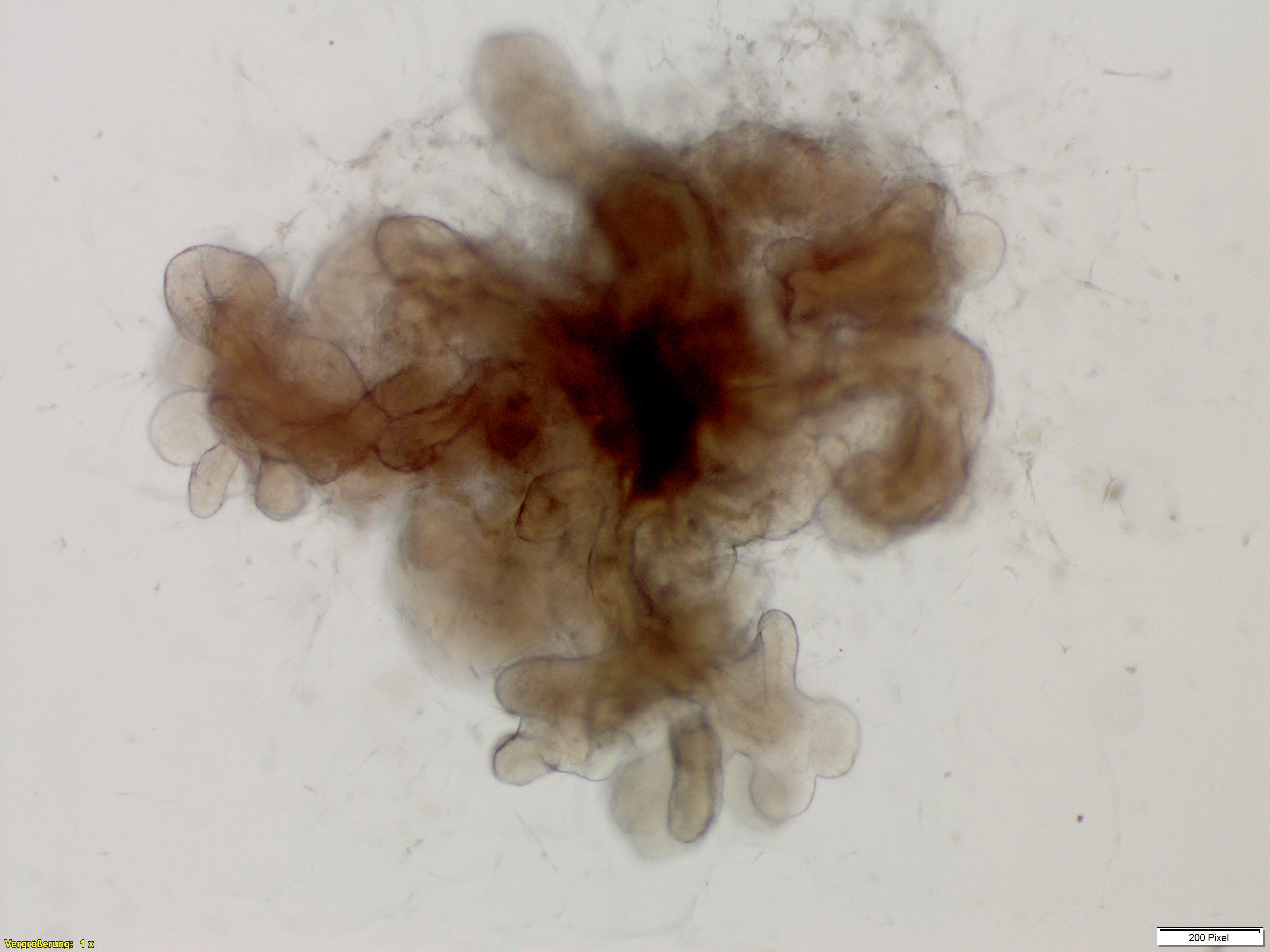
We establish complex intestinal organoids from stem cells as multicellular 3D in-vitro microtissues. Using a special cultivation method, we can even produce inside-out intestinal organoids.
Intestinal Organoids

Our development: inside-out intestinal organoids for investigation of substance uptake, metabolism and immune reactions
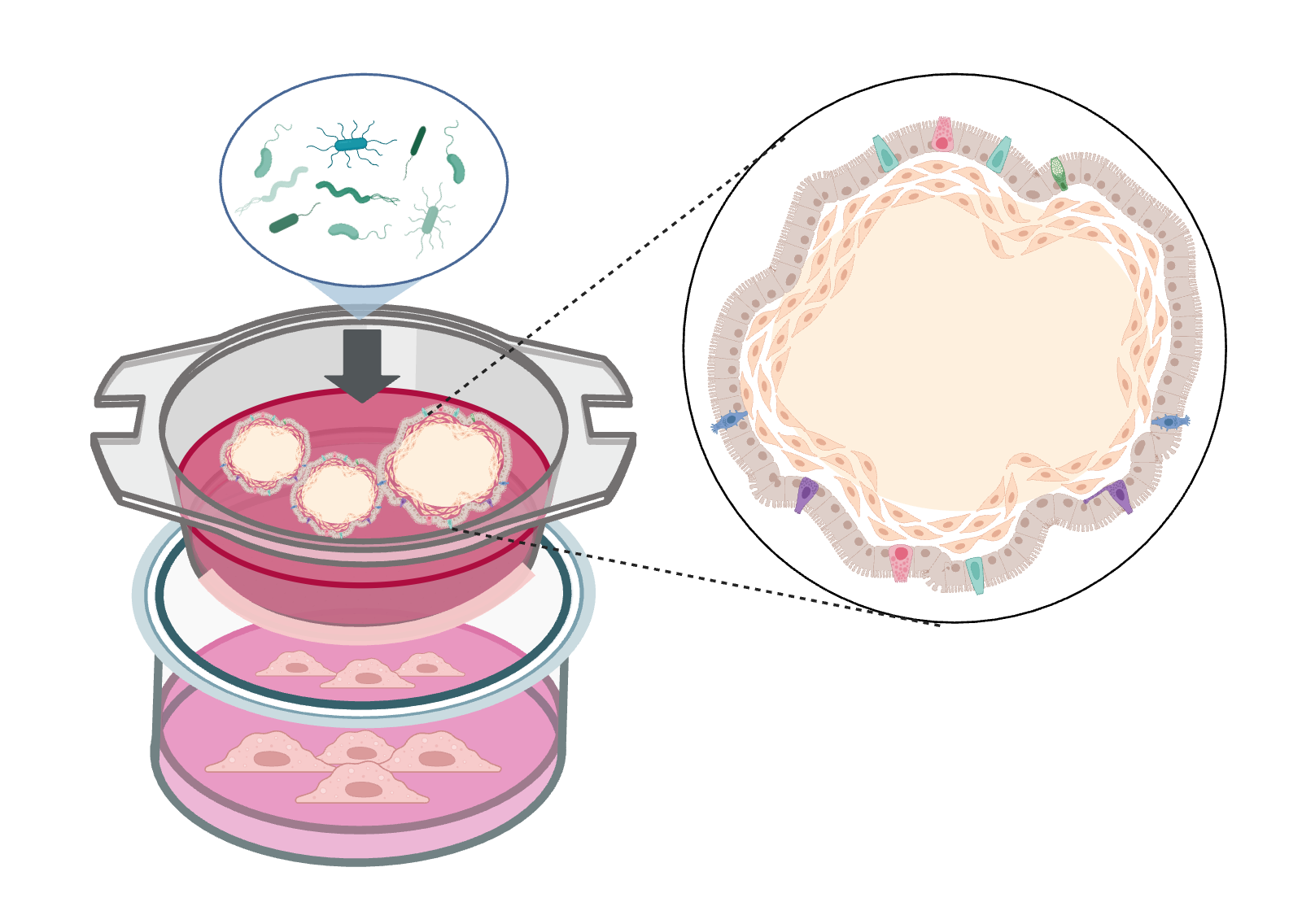
Our inside-out intestinal organoids are complex intestinal organoids based on induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) with the apical side facing the intestinal lumen (apical-out organoids). This access to the apical epithelium is of utmost importance for investigating the absorption and metabolism of drugs, innate immune reactions and barrier function. The investigations are carried out by means of cultivation in suspension without binding the organoids to a matrix.
Supplemented by microbiota (e.g. commensal bacteria of the normal intestinal flora and/or pathogenic bacteria) and immune cells (e.g. macrophages), these organoid models also allow investigations into interactions between host and microbiota or microbial pathogenesis.

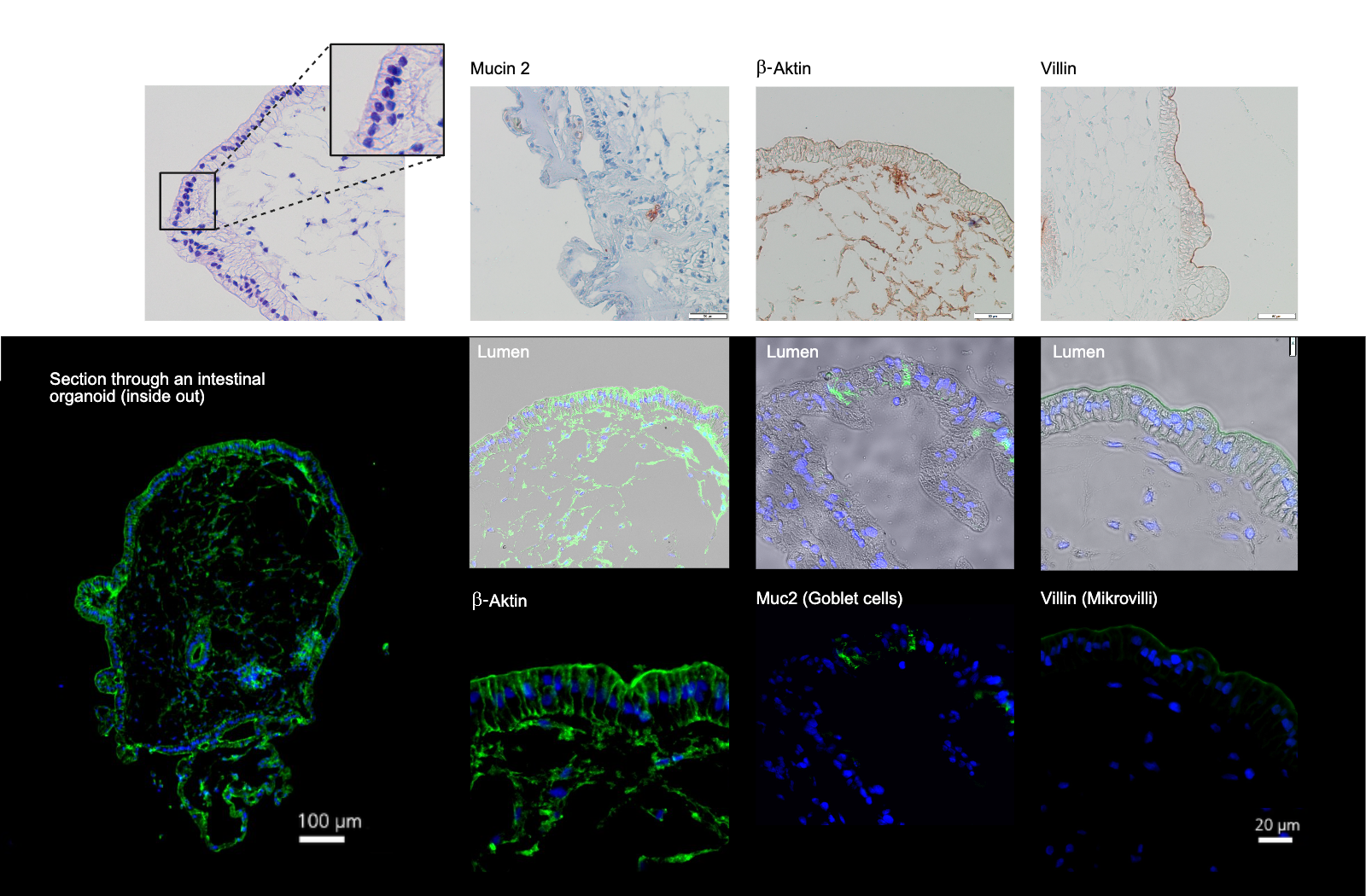
Intestinal organoids representing the in-vivo situation
Our intestinal organoids – with a single-layered epithelium and an underlying connective tissue with fibroblasts – correspond to an in vivo-like tissue structure and precisely display intestinal epithelium-specific protein markers:
- Mucin 2
- β-Actin
- Villin
Applications
Our intestinal organoids can be used, for example, to investigate intestinal toxicity, immune response, interactions between host and microbiota (pathogenic and commensal microorganisms), the positive effects of pre- and probiotics and the mechanisms of action of active substances for intestinal-associated diseases. For example, we have investigated the effect of probiotic bacteria on intestinal models infected with Bacillus cereus.
With our intestinal organoids as in-vitro test systems, we address various applications for
- Assessment of the efficacy and safety of drugs and chemicals (development and preclinical testing)
- Determination of toxicity
- Analysis of transport processes and absorption of a substance
- Disease research
Tabbed contents
Portfolio
Our portfolio of organoids
We provide specifically suitable 3D microtissues for various issues and applications:
- 3D Intestinal organoids
- 3D Inside-out intestinal organoids
- Immunocompetent supplementation of organoids by cultivating immune cells
- Microbiome and infection organoids with bacteria, fungi and viruses
Our services
Range of services
We offer the following services relating to our 3D microtissues, which we carry out in state-of-the-art laboratories on behalf of and in collaboration with customers:
- Conducting studies and substance screenings
- Development of complex organoids including
- Cultivation of organoids from stem cells
- Establishment of complex organoid test systems, supplemented by microorganisms or immune cells depending on the issue at hand
- Phenotypic and functional characterization of models
Analysis methods
Analysis methods
In our 3D microtissues, the effects of chemicals, active substances and products on the architecture of the tissue and physiological properties can be investigated. We offer the following analysis methods:
- Vitality measurements, for example using the MTT test (colorimetric test), alamarBlue(TM)
- Multiplex analysis for the detection and quantification of secreted proteins such as cytokines, chemokines, growth factors and antimicrobial peptides
- Histological and immunohistochemical staining of tissue thin sections
- Protein analyses using Western blot
- Analysis of specific signaling pathway activation via reporter proteins
- RNA and DNA analyses using PCR or qPCR and sequencing
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB