In nature, most of the organic and inorganic substances which are used as starting materials for products are mixtures of substances. Chemical synthesis also usually produces mixtures of substances or products that are contaminated with by-products. A key task in most processes in chemistry and biotechnology is therefore the separation of molecules from mixtures, either to obtain or purify substances or to remove interfering by-products.
Fraunhofer IGB has established a wide range of different separation processes and has the corresponding apparatus and equipment available both on a laboratory and pilot scale. Membrane and adsorption processes, electrophysical and thermal processes, but also crystallization, extraction and chromatography processes are constantly being further developed and optimized for various applications within the scope of our own research work.
A unique selling proposition of our institute is the possibility to combine these processes flexibly – if necessary with other classical processes such as centrifugation or flotation – and to integrate them into process chains. This know-how can also be used for water treatment, recycling or in food processing technology.
Technology platform: Separation technologies
Established separation technologies
Membrane processes
At Fraunhofer IGB we develop novel membranes for the treatment of aqueous solutions (membrane adsorbers for the separation of micropollutants or heavy metals, membranes for forward osmosis) and for gas separation (separation of O2). In addition, we are working on the development of membrane reactors that allow the direct integration of chemical reactions with substance separations.
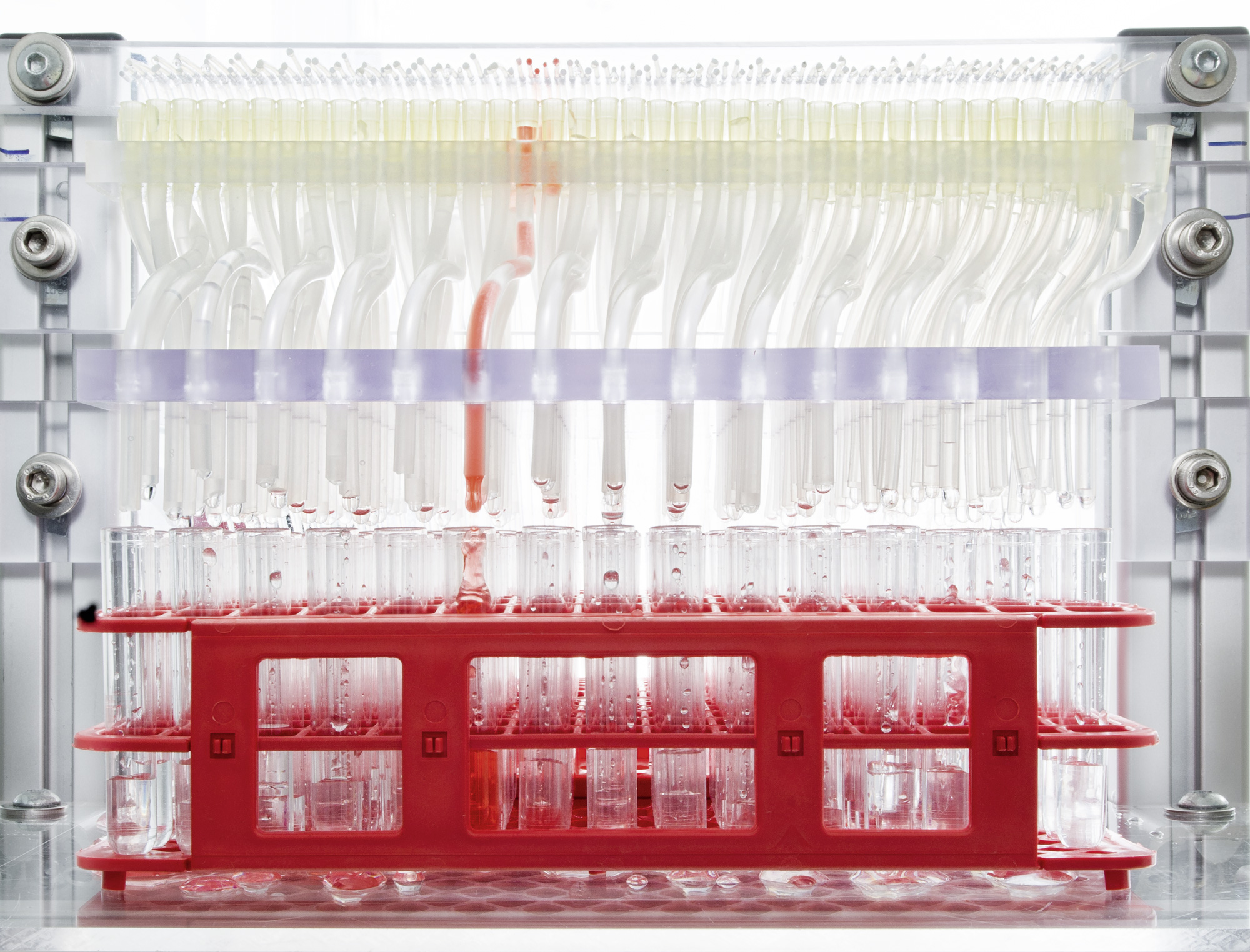
Adsorption processes
At Fraunhofer IGB, polymer particles with functional surfaces are developed to selectively bind valuable substances or micropollutants. For this purpose, proprietary polymers are processed into particles, e.g. by miniemulsion polymerization. However, biomaterials such as chitosan can also be specifically functionalized.
Thermal separation processes
In these process developments, too, we pursue the goal of achieving the highest possible efficiency. An important factor here is the combination of functionalities in a single process step. An example of this is drying with integrated recovery of volatile substances.
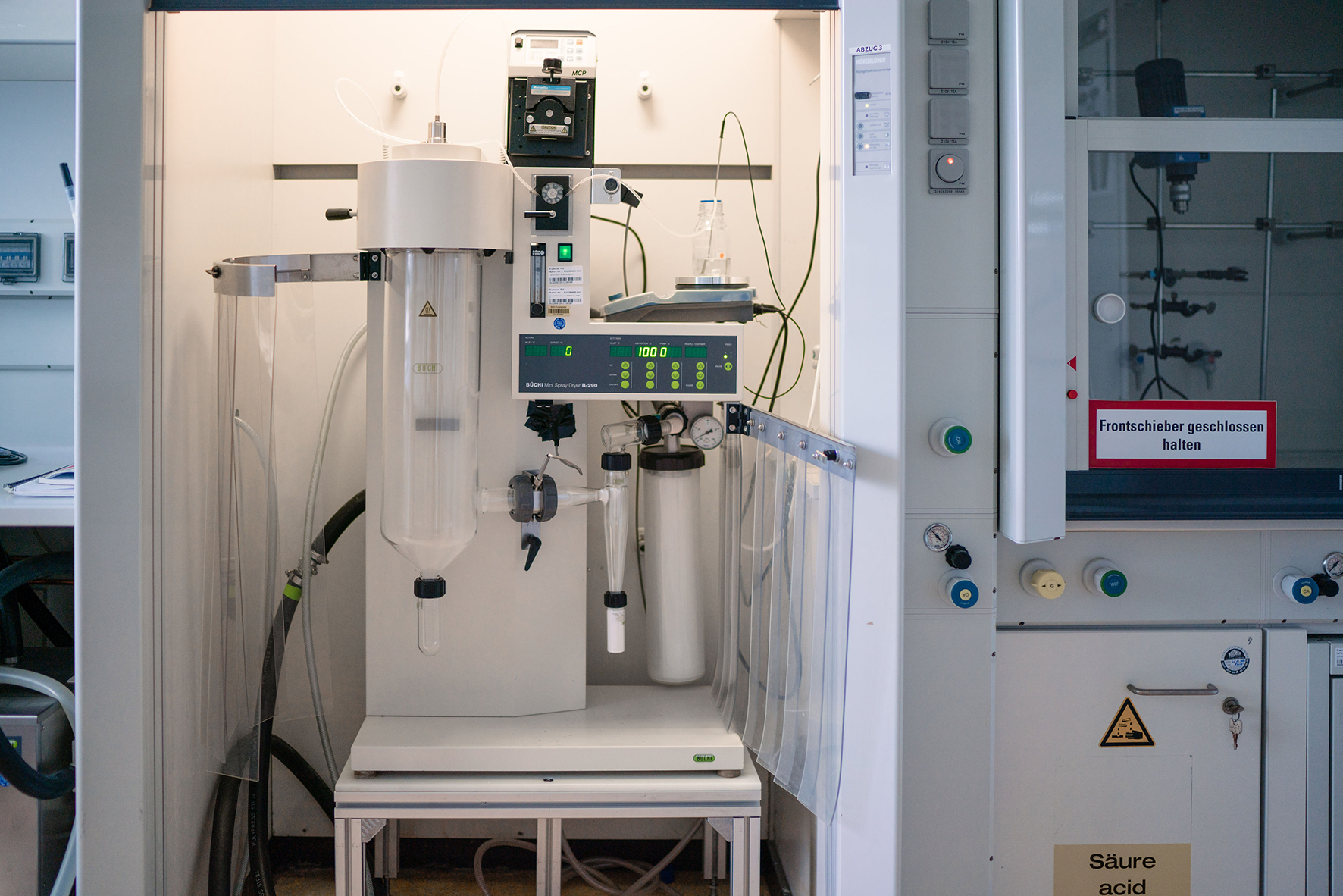
Drying technologies
In addition to the above mentioned superheated steam drying (SHS) process, we use other drying technologies such as drying by various evaporators, freeze drying and spray drying. At the Fraunhofer IGB in Stuttgart, we have laboratory facilities for evaporation, freeze drying and spray drying of small quantities in the milligram to gram range for feasibility studies as well as drying of smaller sample quantities. We are happy to investigate customer-specific substrates as part of a feasibility study and offer the drying of sample quantities as a service.
At Fraunhofer CBP in Leuna, we can also concentrate larger quantities gently under vacuum (300 L/batch) and subsequently dry further under vacuum (30 L/batch in the cabinet dryer or 600 L/batch in the vacuum filter dryer) as well as spray drying (7.5 kg/h) or freeze drying (24 L/batch). Larger drying capacities, also under hygienic requirements for the food sector, we then develop via our partner network.



Compound separation by electric fields
In a number of processes newly developed at IGB, the separation of substances is based on the interaction of charged particles with an electric field. The movement of ions and molecules in the electric field is largely determined by their charge and mobility. This means that their separation is based on electrophoretic properties. The IGB designs various processes for different applications, tailored to the requirements of the respective separation problem, e.g. free-flow electrophoresis, electro-membrane filtration and electrodialysis.
Extraction technologies
Liquid extraction is used to extract valuable substances (biosurfactants, itaconic acid, malic acid, xylonic acid, long-chain dicarboxylic acids, furan dicarboxylic acid) from fermentation broths.
For the extraction of ingredients from microalgae, we at the Fraunhofer IGB have established pressure liquid extraction (PLE) as a batch high-pressure process. Algae constituents of different polarity are extracted with solvents or solvent mixtures of corresponding polarity at temperatures up to 150°C. The scale-up of the technology is currently under way.
Chromatography
Biosurfactants and basic chemicals produced by fermentation are purified by chromatographic methods. Mannosylerythritol lipids, for example, are first obtained by separation and extraction from the fermentation broth. To separate oily residues, the extract is processed by chromatography (stationary phase: silica gel, mobile phase: solvent).
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB